Understanding ChatGPT Plugins: Benefits, Risks, and Future Developments
This article covers how plugins work, the necessity that drove their integration into ChatGPT, and the transformative impact they'll have on the ChatGPT user experience.
Expect improvement, not perfection.
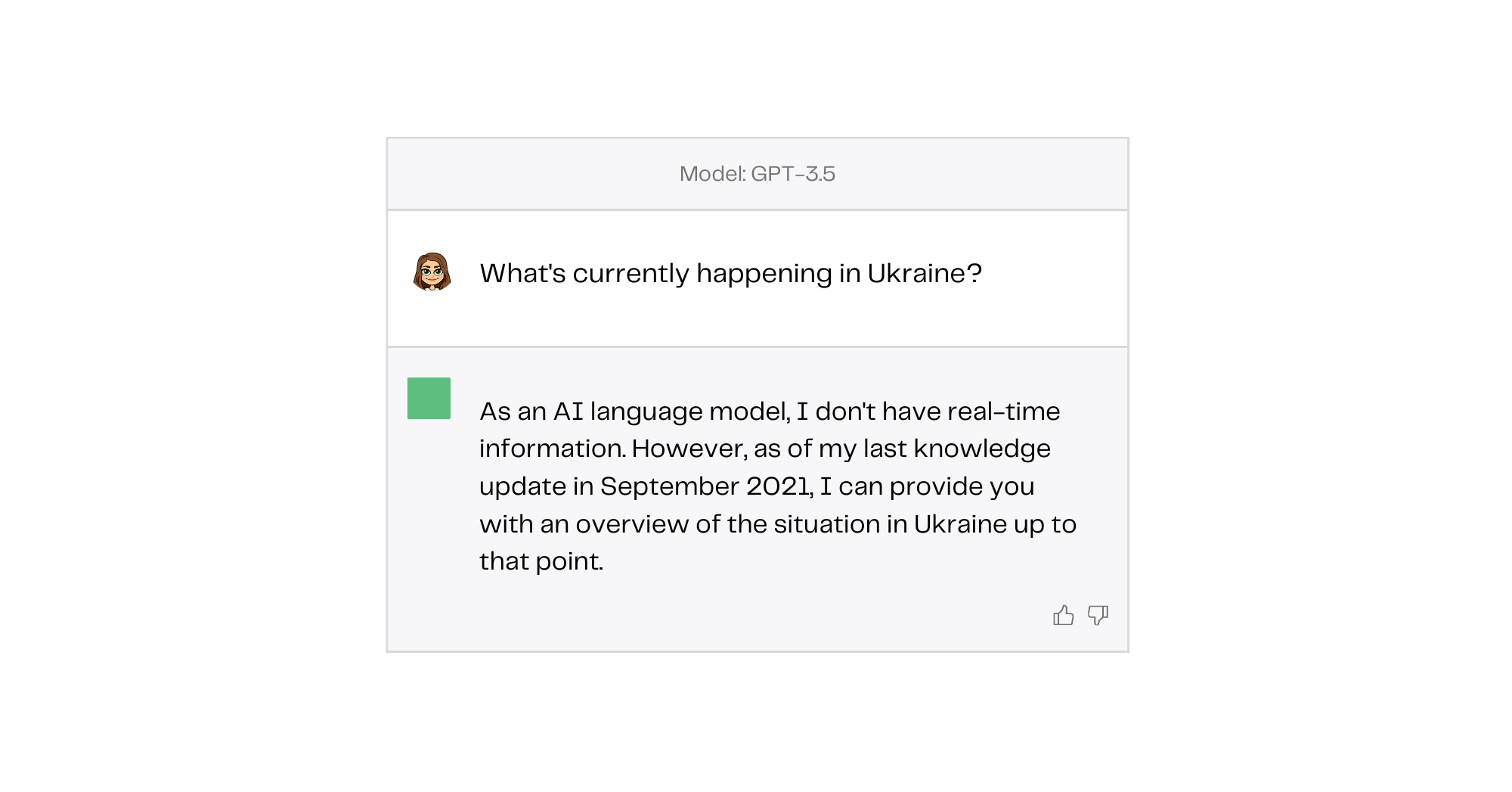
When ChatGPT was first released in late 2022, its capabilities were simultaneously impressive and unimpressive. It could rap battle and write differential equations in LaTeX but didn’t know anything about the war in Ukraine and sometimes couldn’t even do simple math. The stark contrast between its capabilities and limitations, while confusing and sometimes mystical, made for some interesting Twitter threads, but ultimately underscored the model’s dire need to be connected to the internet.
But plugins don’t just connect ChatGPT to the internet, they can also connect it to other external data sources, like an internal database or even your email inbox. Essentially, plugins expand the capabilities of ChatGPT, increase the accuracy of its responses, and allow for a more personalized chatbot experience.
This article covers how plugins work, the necessity that drove their integration into ChatGPT, and the transformative impact they'll have on the ChatGPT user experience. We'll also examine the risks and limitations associated with these plugins and speculate on what the future might hold for ChatGPT and its evolving plugin ecosystem.
What are plugins?
Plugins are software add-ons that customize and extend the capabilities of an existing program. These small additions, oftentimes created and published by third-party developers, are meant to fulfill specific needs defined by the user that are beyond the scope of the original product.
You’re probably most familiar with browser plugins, also referred to as extensions. Google Translate, for instance, offers a plugin for Chrome-based browsers that can translate an entire webpage with just the click of a button. AdBlock, on the other hand, is a plugin offered by a third-party developer that blocks pop-ups, removes ads from webpages and applications, and disables intrusive trackers. Both of these plugins meet specific needs of users by adding functionality to the browser.
While plugins can be incredibly useful and quick to download, it’s important to remember that many are published and maintained by third-party developers. This means that the quality of plugins for a given application can vary tremendously and you should always be sure to independently verify their safety.
Now that we’ve reviewed what exactly a plugin is, let’s discuss its functionality in the context of ChatGPT.
ChatGPT without plugins
ChatGPT is a large language model (LLM) developed by OpenAI, designed to work as a chatbot assistant, generating human-like conversational output (responses) in response to text input (prompts).
Although up for debate in the machine learning community, the easiest way to explain ChatGPT is to say that it is a statistical model that is trained to predict the next word in a series based on the words it’s seen so far (like predictive search) and based on the data it’s been trained on.
During the training process, the model is fed a massive amount of text data. The model learns the underlying structure of the training data by studying the intricate patterns, relationships, and dependencies between different texts. This means that when you receive a response from ChatGPT, it's not pulling specific information from a defined source. Instead, it's making an educated prediction based on the input you've provided and the data it was trained on. The response you receive is an approximation, designed to mirror what the information might be, rather than a direct retrieval of concrete data.
However, because the model isn’t hooked up to the internet or any other sort of external data source, it can spit out wildly inaccurate information in a very convincing way. For example, when I ask ChatGPT to give me the titles of five influential papers on the topic of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, three of the articles it suggests don’t even exist.
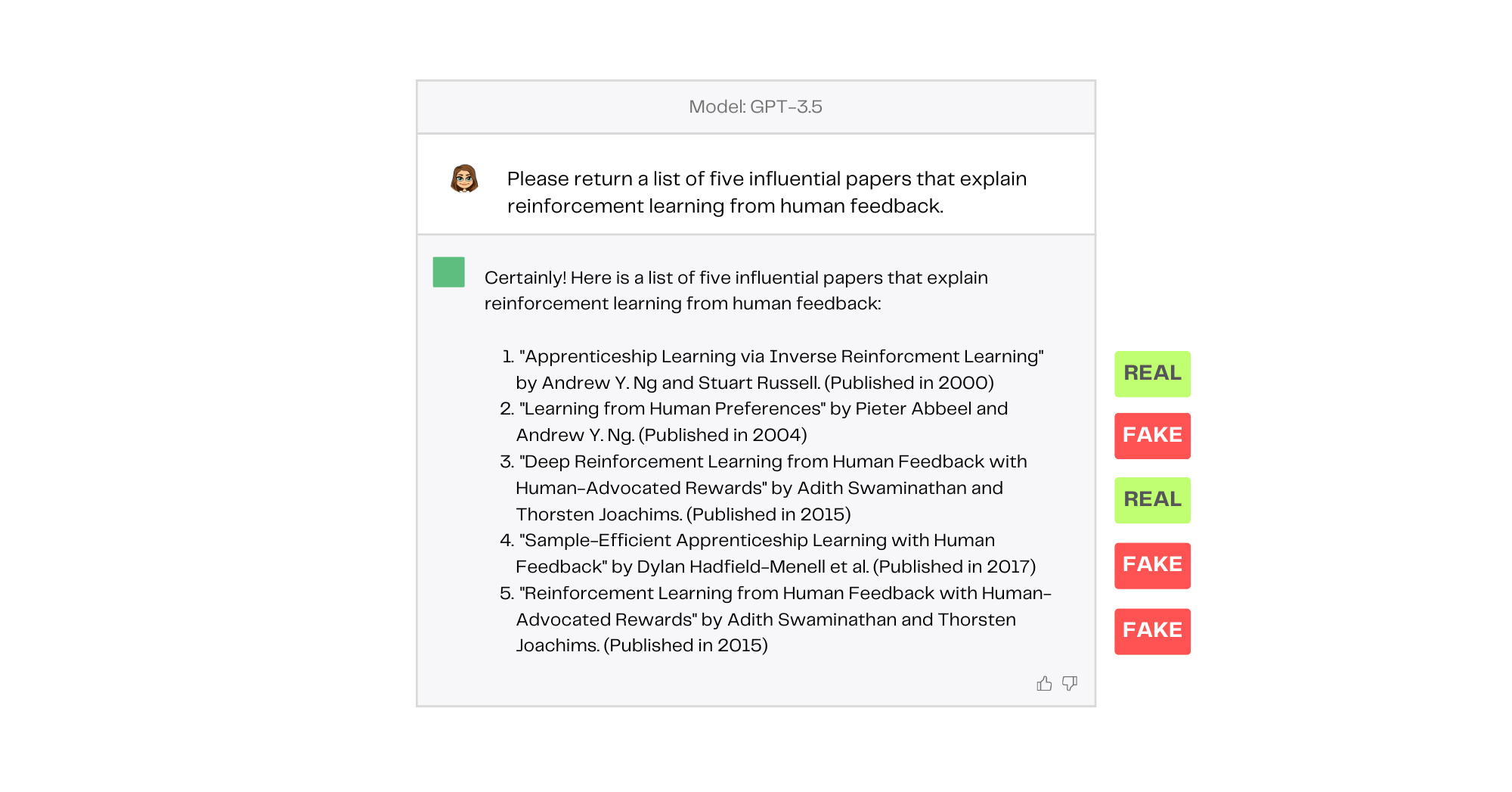
Perhaps the most concerning aspect of this response is that the imaginary papers sound totally plausible. They are even attributed to well-known authors in the field. This is called hallucination and it’s one of the most serious flaws of LLMs. While there are several machine learning methods that can reduce hallucination in LLMs, enabling these models to connect to data sources through the use of plugins is a lower-cost way to increase accuracy and further expand the capabilities of LLMs.
ChatGPT with plugins
ChatGPT plugins enhance the chatbot experience by providing the underlying language model with recent, personal, or specific data that was not included in the model’s training data. The connection of the LLM to real-time data sources, like databases or web browsing, is aimed at helping ChatGPT produce more accurate and timely results. It also allows the chatbot to perform more complex tasks, like responding to an email, directly within the ChatGPT interface. Let’s break down all this added functionality into different categories.
Web browsing
The introduction of ChatGPT's Web Browsing mode allows you to conduct research and search the internet without using a search engine and clicking on links. The purpose of this new functionality is to streamline your search process and internet browsing experience, cutting out manual tasks like vetting results, clicking on links, and scanning those web pages for the desired information.
To accomplish this, ChatGPT essentially rephrases your prompt into a search query, performs an internet search, clicks on the most relevant link, reads the webpage, and responds with your desired information. Let’s look at how ChatGPT in Web Browsing mode answers the question “Who is running for President in the US 2024 election?”
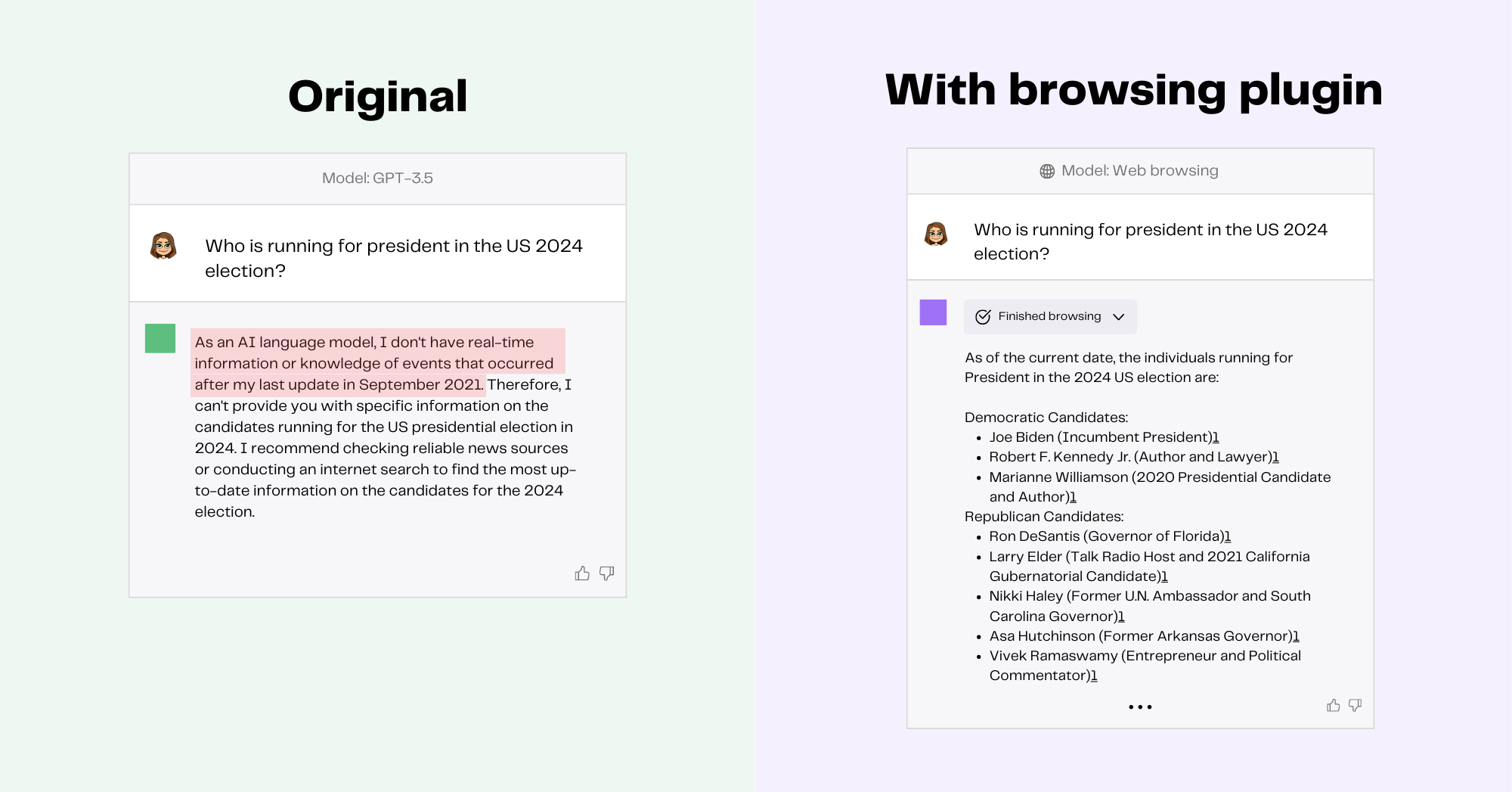
Whereas the original version of ChatGPT would simply punt on such a question, web browsing capabilities enable ChatGPT to provide relevant, timely information on events that occurred after the training cutoff for the base model. Browsing Mode is also capable of citing its sources, including links to online sources used to gather information, which allows the user to independently verify parts of ChatGPT's responses.
Ultimately, connecting the natural language capabilities of a large language model to external data sources, namely the internet, leads to a more informed and comprehensive experience.
Task automation
While Browsing Mode is helpful for relatively simple tasks involving research and information gathering, ChatGPT's new custom plugins really take it to the next level, allowing it to automate multi-step tasks on a personalized basis.
Task automation, the act of using technology to complete a task instead of completing it by hand, is nothing new. You encounter it whenever you use self-checkout at the grocery store, check-in kiosks at the airport, or send your robot vacuum on a mission to clean up the kitchen after dinner. Digital task automation uses software to automate routine and repetitive tasks, like sending automatic email responses when you're out of the office.
Incorporating LLMs into digital task automation workflows can lead to even more effective and personalized automation of common tasks. Here’s what happens when we use the Zapier plugin and ask ChatGPT to write an email to my mom. To complete this task, ChatGPT asks Zapier (which is already connected to my Gmail account) to draft an email with all the relevant information (topic, recipient, tone) provided in the prompt. Zapier completes the task, using the ChatGPT language model to generate all the necessary text, and provides a link that allows me to review and send the draft directly from my Gmail account.
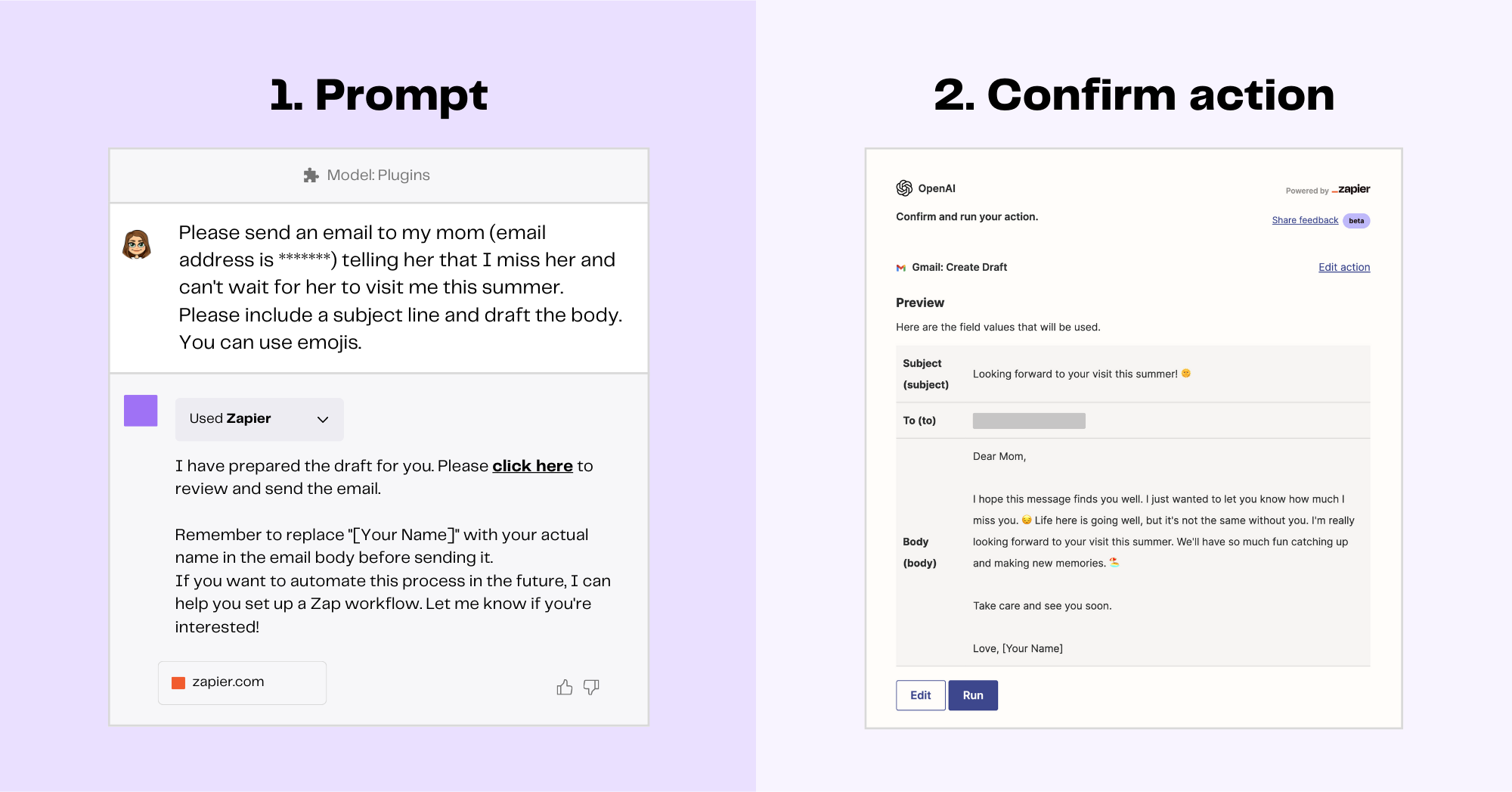
The idea behind automating tasks with ChatGPT is that, in theory, you can perform any number of tasks without having to open a bunch of tabs, click through things manually, and compose your own text. Not only does this save time on a case-by-case basis, it also delivers valuable results at scale. For instance, if you regularly send and receive over a hundred emails per day, using a set of pre-defined prompts with ChatGPT and the Zaiper plugin could save you a significant amount of time.
Incorporating LLMs with plugins for task automation presents an exciting opportunity to transform the way we handle both mundane and complex tasks. Here are a few examples:
- Query and update documents and databases in a conversational way
- Automate the creation and posting of social media content
- Automate personal and professional correspondence
- Schedule and cancel appointments and work calls
- Generate recipes and meal plans based on specific requirements
- Plan vacations and activities based on certain criteria
- Summarize findings from a given dataset
- Write code for a specific task in a given project
Drawbacks and limitations
While plugins can help expand the existing capabilities of LLMs, they also come with their own drawbacks and limitations. Here are the most impactful limitations I experienced while using ChatGPT plugins:
- Plugins are slow. In simple use cases, like looking up real-time information, it may still be quicker to just use a search engine.
- Plugins can still hallucinate. Hallucinations might be reduced, but remember that the underlying LLM behind ChatGPT can still hallucinate.
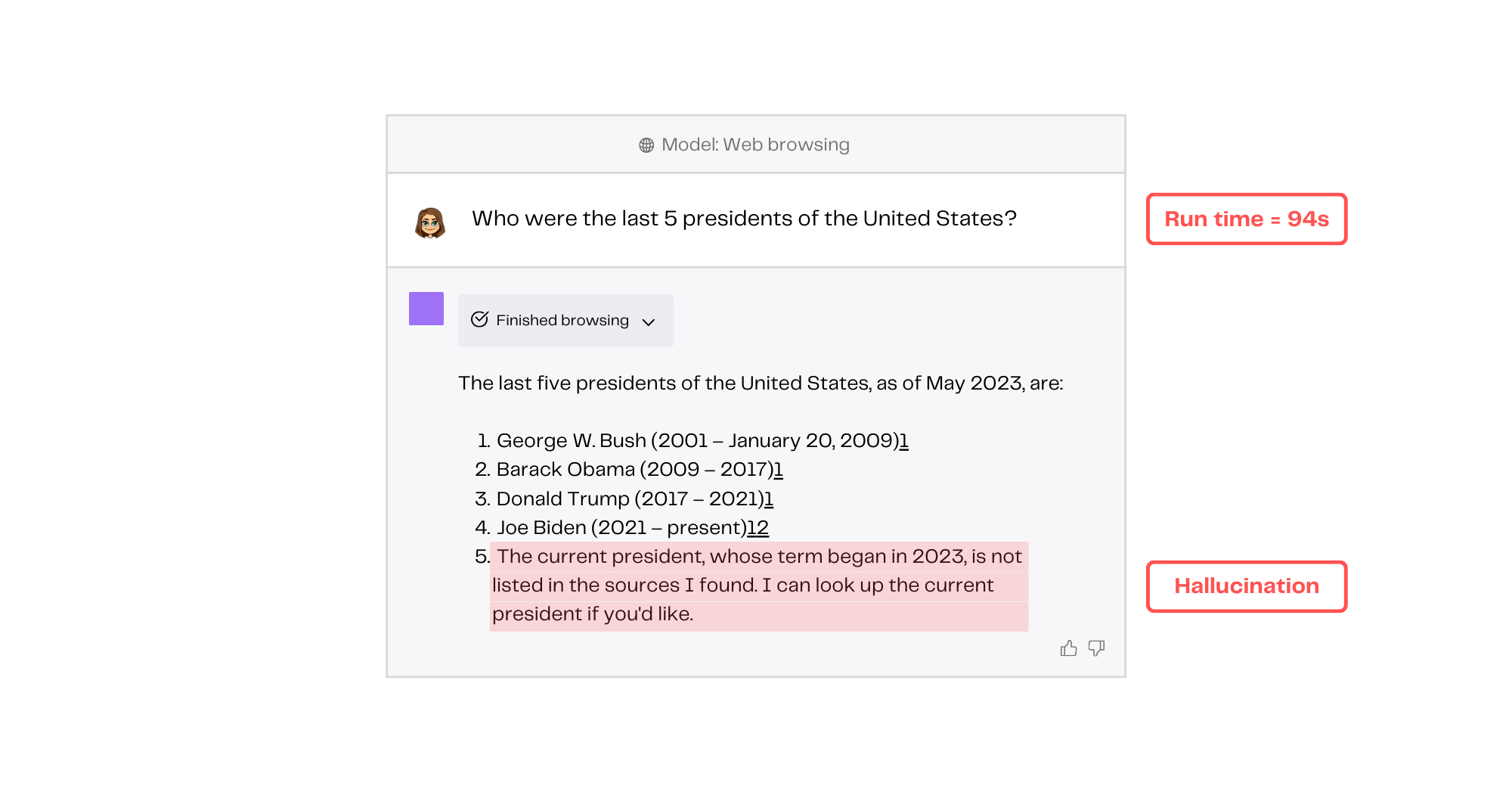
- Plugins can be brittle. Plugins rely on external APIs, meaning that if an API is down or not functioning properly, it can render a plugin nearly useless. This happened to me more than a few times.
- Plugins expose more of your personal data. In order to reap the benefits of using LLMs with your own personal data, you need to expose that data to the plugin. Make sure to read the data privacy policies of each plugin you use before integrating them with personal data, documents, or your email account.
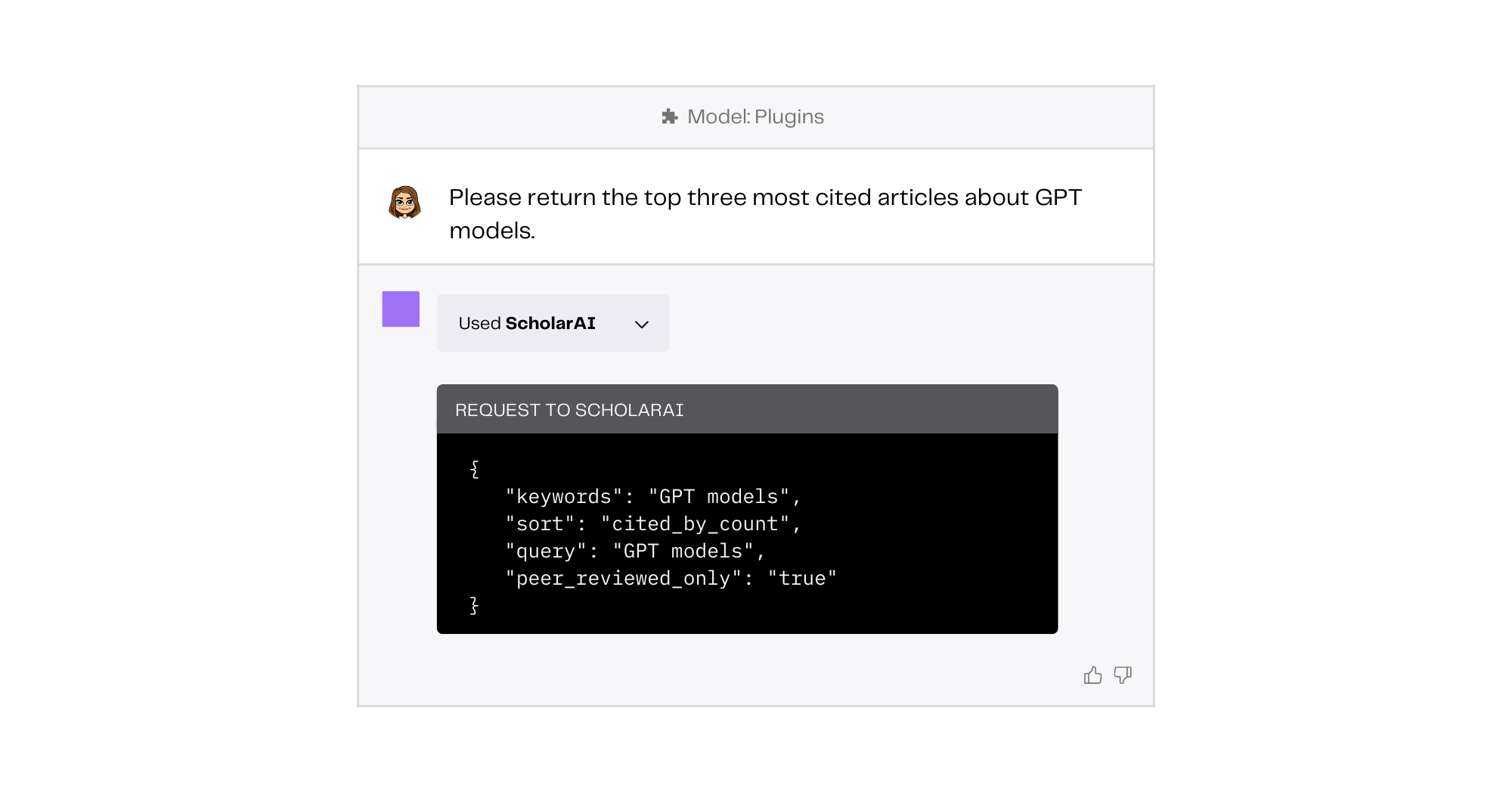
- Some plugins are not that complex. When you look under the hood of some plugins by clicking on the dropdown menu for the plugin that’s used to elicit your response, you can see that some plugins aren’t that complex. For example, when using the ScholarAI plugin to search for articles, it simply extracts a search query with simple parameters from the prompt and then searches a database.
- Plugins lack human judgment. ChatGPT’s Browsing Mode and other plugins that connect users to real-time data are searching the internet for us, effectively “clicking” on links and scanning those web pages for relevant information. This can’t replace the judgment of a human because we don’t know the decision-making process behind how sources are chosen or prioritized.
Most promising ChatGPT plugins
Now that we’ve reviewed how ChatGPT plugins work and named their limitations, let’s take a look at some of the most promising ChatGPT plugins. Although still in their infant stage, these plugins have a wide range of capabilities and potential to automate diverse tasks that will either save you a significant amount of time or deliver serious business value.
Zapier
Zapier is a workflow automation platform that supports thousands of popular apps, connecting them to each other and executing automated tasks. Originally, you would have to manually configure these tasks on the Zapier website; now, you can do that just by prompting ChatGPT.
In a previous example, I showed how to use Zapier to draft a personal email. Now, let’s use the plugin to add automatically add new data to an existing Google Sheets document. For simplicity, let's say the spreadsheet holds the names, breeds, and ages of all my favorite dogs. After installing and enabling the Zapier plugin, all I need to do is tell ChatGPT in plain English to add data to an existing Google Sheet called "favorite-dogs." Next, I click on the link provided in the response, confirm that ChatGPT understood my request correctly, and confirm the action. When I open my "favorite-dogs" document, I'll see that the data was added.
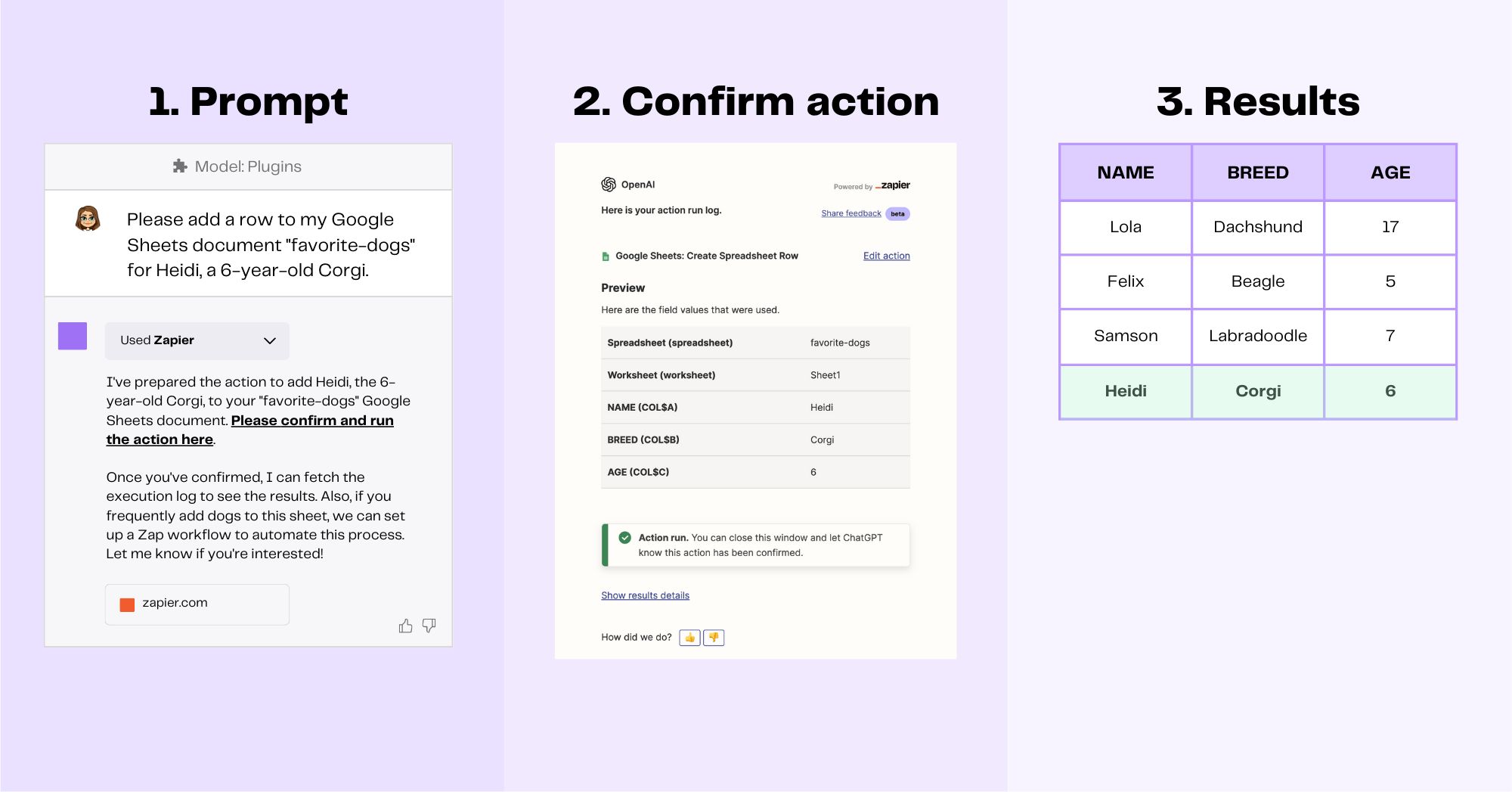
Zapier maintains a list of creative ways to connect different applications for accomplishing tasks with ChatGPT, including tasks like converting new Dropbox files to PDFs and generating document summaries, generating replies to incoming SMS messages, and prioritizing tasks based on Evernote to-do lists.
The Zapier ChatGPT plugin has incredible potential for automating menial and repetitive tasks. It performs tasks relatively quickly and gives you an overview of what it’s about to do before it does it. However, before using this plugin, I recommend reviewing Zapier’s OAuth policies, which specify the different levels of access and permissions to your external accounts (e.g. Gmail, Google Drive) you give to Zapier to perform tasks on your behalf.
Noteable
Noteable is a collaborative data science notebook platform for Ad-hoc analysis, machine learning, and data apps. Like Jupyter notebooks, Noteable is the place where you can write code to clean, summarize, and visualize data as well as train and evaluate machine learning models. The Noteable ChatGPT plugin allows you to interact with existing data and notebooks and even create new notebooks just by prompting ChatGPT. This means that you can get insights and performs tasks with real-life data without writing a single line of code.
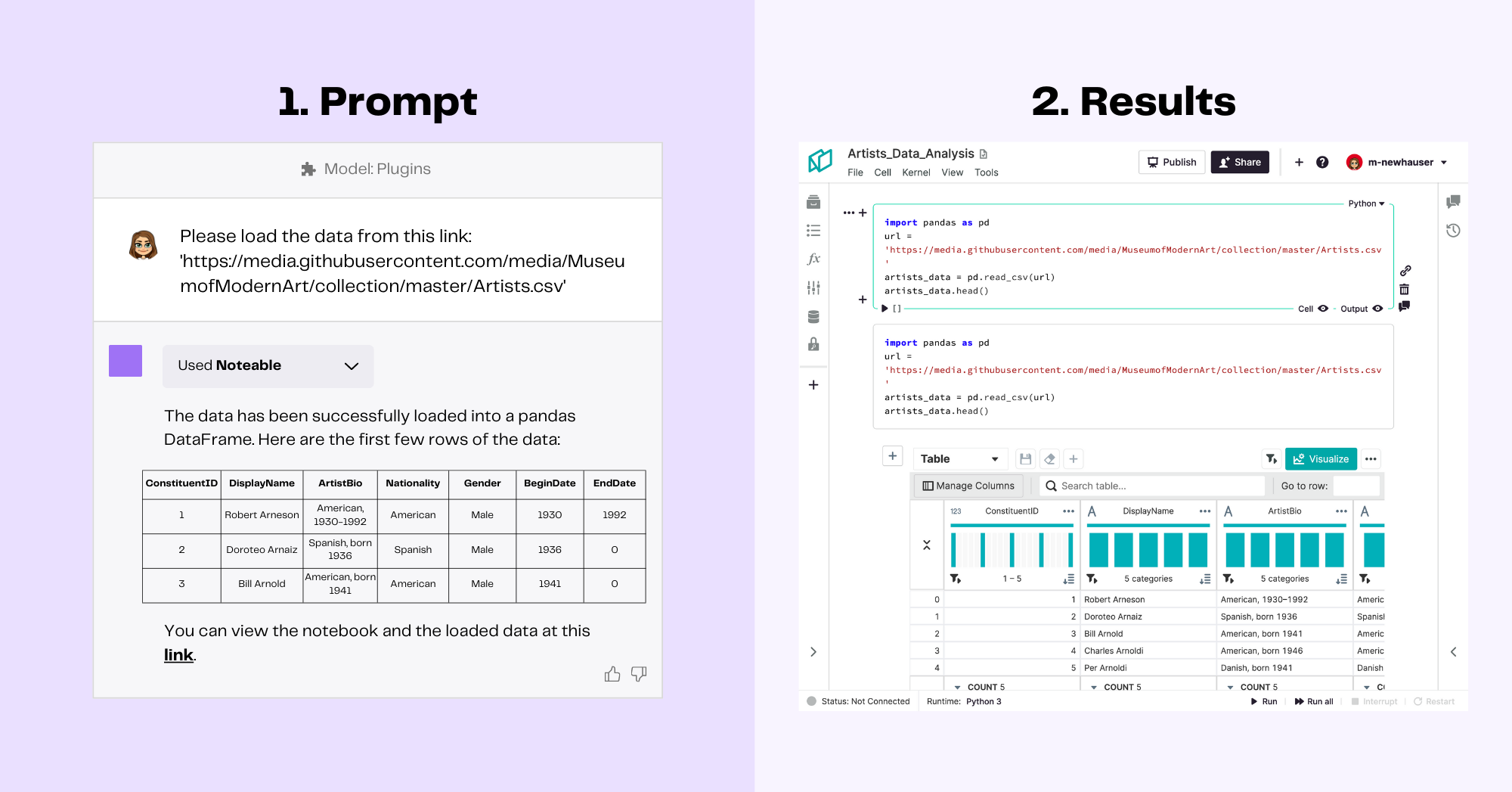
With the Noteable plugin, you can also use natural language to query databases hooked up with Noteable, clean and transform raw data using Pandas, load data from external sources, and even create plots. For other creative ideas, check out these examples of notebooks created by the Noteable team using the ChatGPT plugin.
To be on the safe side, I would not use this plugin with sensitive company or personal data. However, if you’re an aspiring data scientist seeking an engaging and inventive method to enhance your skills, or if you’re working on a project that involves public code and data, this plugin could be an enjoyable tool to explore!
Current landscape of ChatGPT plugins
Plugins expand the capabilities of LLMs, like ChatGPT, by allowing them access to information not included in their original training data. This gives large language models the potential to be both more accurate and better at task automation. Some of the first available ChatGPT plugins, like Zapier and Noteable, show great promise, allowing users to execute tasks of varying levels of difficulty with simple prompts.
However, plugins for LLMs are still very much in their nascent phase. The first generation of ChatGPT plugins are slow, a bit clunky, and sometimes don’t even work. Think of these plugins as similar to the first iOS and Android apps to hit the market in 2008. Developers are learning how to write code that interacts with users in new ways and fulfills new needs. Future plugins will likely be faster, more sophisticated, and more user-friendly.
However, it’s important to remember that connecting LLMs to the internet and external data sources come with risks of their own. Language models lack human judgment when it comes to vetting internet sources, meaning that we need to exercise caution and skepticism when we let a chatbot browse the web for us. Similarly, users need to be aware of the personal data they are forfeiting to third-party plugins, as these plugins may collect, store, or even share this data in ways that the user may not fully understand.
The future of ChatGPT plugins
First and foremost, the complexity and performance of ChatGPT plugins will improve. Third-party APIs will (hopefully) become more reliable as companies devote more resources to maintaining them and plugins will eventually be able to perform tasks faster (although perhaps only for paying customers).
Second, the number and diversity of plugins will increase dramatically in the coming months. Because plugins are a fun and productive way to build engagement with digital products and content, you can bet that many companies will be investing resources into developing innovative and interactive plugins for ChatGPT. And since all you need in order to start developing your own plugin is to sign up for OpenAI’s plugin developer access (there’s currently a wait list), the open source community has the potential to contribute all sorts of creative plugins.
Finally, it’s important to remember that the future of ChatGPT may not, in fact, be ChatGPT. The quantity and quality of various degrees of open source chatbot assistants and models is increasing so quickly that I’ve nearly given up keeping track. With such a concerted effort from the open source community to keep LLMs transparent and accessible, combined with the uncertain future of AI regulation both in the United States and in Europe, it’s hard to tell what the future will look like.
With that being said, have fun toying around with all the new ChatGPT plugins and be careful which data you choose to share!
References
(1) A. George, What Are Plugins, and How Do They Work? (2021). Lifewire.
(2) K. Olang, Mozilla Firefox Opening to a Blank Page (2023). Chron.
(3) T. Ngo, ChatGPT is NOT simply “predicting” the next word (2023). LinkedIn.
(4) F. Neugebauer, Understanding LLM Hallucinations (2023). Towards Data Science.
(5) K. Eby, Automate Everything: The Ultimate Guide to Task Automation (2018). Smartsheet.
(6) E. Alston, New! Try Zapier’s ChatGPT plugin (2023). Zapier.
(7) U. Sharma, 125+ Best ChatGPT Prompts for All Kinds of Workflow (2023). Beebom.
(8) Zapier. Do more with ChatGPT integrations (2023). Zapier.
(9) Zapier. Convert new Dropbox files to PDFs with PDF.co and summarize them with ChatGPT (2023). Zapier.
(10) Zapier. Generate replies to new incoming sms77 messages with ChatGPT (2023). Zapier.
(11) Zapier. Get ChatGPT to prioritize your day based on your to-dos (2023). Zapier.
(12) Noteable. ChatGPT Plugin (2023). Noteable.
(13) Noteable. ChatGPT Plugin Examples (2023). Noteable.
(14) OpenAI. Chat plugins (2023). OpenAI.
(15) OpenAI. ChatGPT Plugins waitlist (2023). OpenAI.
(16) S. Raschka, Ahead of AI #8: The Latest Open Source LLMs and Datasets (2023). Ahead of AI.
(17) A. Engler, The EU and U.S. diverge on AI regulation: A transatlantic comparison and steps to alignment (2023). Brookings.
Related articles
Related resources




